Introduction
Time-based media has revolutionized the way we experience art and information. Unlike traditional static forms such as paintings or sculptures, time-based media relies on the element of time to unfold its narrative or experience. This dynamic form of media engages viewers in a process that evolves, making it an intriguing field that spans across various types and representations. In this post, we’ll explore what time-based media is, the different types it includes, examples of sources, and how it is represented.
What is an Example of Time-Based Media?
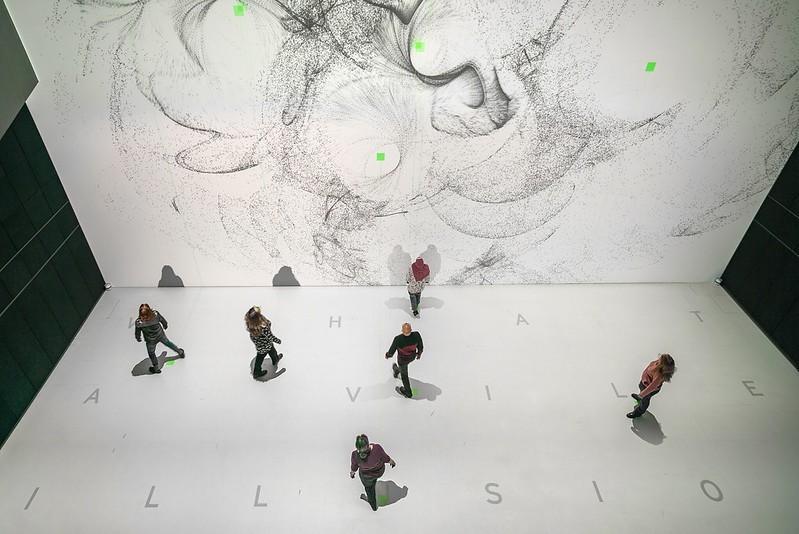
An example of time-based media is a video installation. Video installations are artworks that use video technology to create immersive experiences for viewers. Unlike a traditional painting that is immediately grasped at a glance, a video installation unfolds over time, often telling a story or creating an evolving visual and auditory environment. These installations can range from simple loops to complex narratives that require the audience to watch for extended periods to fully appreciate the piece. This reliance on the dimension of time to convey meaning is what makes video installations a quintessential example of time-based media.
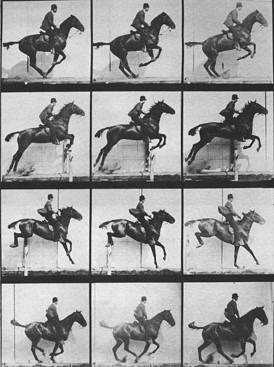
Eadweard Muybridge, Sequence of a Horse Jumping, 1904.
What Are the Types of Time-Based Media?
Time-based media encompasses a variety of forms, each bringing a unique approach to the use of time. Some of the most prominent types include:
Video Art: Video art involves the creation of moving images that may be recorded, live-streamed, or presented as an installation. It often explores concepts like time, space, and movement, using video as a medium to present stories or abstract ideas.
Performance Art: This type of time-based media is live and can incorporate elements like theater, dance, and spoken word. The temporal aspect is crucial, as the performance happens in real-time and often cannot be replicated in the exact same way.
Digital Animation: Unlike traditional animations, digital animations in the context of time-based media are often interactive or generative, meaning they can change based on user input or algorithmic processes, evolving over time.
Sound Installations: These use audio elements to create immersive experiences. Sound installations might involve looping tracks, layered soundscapes, or live sound performances, all designed to be experienced over a period.
Which is an Example of Time-Based Media Sources?
Time-based media can be sourced from a variety of platforms, both physical and digital. One notable example is the Museum of Modern Art (MoMA), which has a dedicated department for film and time-based media art. MoMA’s collection includes works from pioneering video artists as well as contemporary practitioners, making it a key source for time-based media.
Another example of time-based media sources is digital platforms like YouTube or Vimeo. These platforms host vast amounts of time-based media, from independent art films to performance art recordings. They have become essential in the distribution and consumption of time-based media, allowing artists to reach a global audience and enabling viewers to access works that might otherwise be confined to physical galleries or museums.
What is Time-Based Media Representation?
Time-based media representation refers to how these works are presented and interpreted. The way a piece of time-based media is represented can significantly impact how it is perceived by an audience. Key aspects of representation include the duration, pacing, and sequence of the media. For example, a video installation may be displayed on a continuous loop, inviting viewers to join at any point and experience the piece in a non-linear fashion.
Representation also involves curatorial choices, such as the environment in which the media is displayed, the equipment used, and even the physical space’s arrangement. These factors contribute to the overall experience and can either enhance or detract from the work’s impact. Proper representation is crucial, as it helps convey the artist’s intended message and ensures the audience’s engagement throughout the media’s temporal unfolding.
Conclusion
Time-based media is a dynamic and evolving field that challenges traditional notions of how art is created and experienced. Through examples like video installations and digital animations, we see how time-based media leverages the element of time to engage audiences in unique ways. By understanding the types, sources, and representation of time-based media, we gain insight into its power to convey complex narratives and emotions over time. As technology continues to advance, so too will the possibilities within time-based media, making it an ever-relevant and fascinating area of study and appreciation.